The fight against Alzheimer's disease saw significant progress in 2024, offering renewed hope for millions affected by this debilitating condition. Here are five key advancements that shaped the landscape of Alzheimer's research and care:
1. FDA Approval of Kisunla: A New Weapon Against Amyloid Plaques
The FDA's approval of Kisunla (donanemab) marked the third new Alzheimer's drug approved since 2021. This once-monthly injection targets amyloid plaques, protein build-ups in the brain that disrupt cognitive function. Kisunla's unique mechanism allows for therapy discontinuation once amyloid plaques are cleared, a significant step towards more targeted treatment.
The Alzheimer’s Association hailed this approval as "real progress," offering patients more options and potentially more time to manage their condition.
2. Blood Tests: Paving the Way for Faster and More Accurate Diagnoses
Research in 2024 propelled Alzheimer's blood tests closer to mainstream clinical use. Studies demonstrated these tests' high accuracy in identifying the disease, potentially expediting access to clinical trials and appropriate treatments. One study showed a specific blood test achieving 90% accuracy in diagnosing Alzheimer's in patients exhibiting cognitive symptoms.
3. Addressing the Need for Post-Diagnosis Support
A 2024 Alzheimer's Association survey highlighted the critical need for improved support systems for newly diagnosed individuals and their caregivers. A staggering 97% of caregivers expressed a desire for such resources, with a majority citing care coordination as a major stressor. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services responded by launching the GUIDE model, an eight-year pilot program designed to enhance dementia care management and support patients within their communities.
4. Wildfire Smoke: An Emerging Environmental Risk Factor
A decade-long study presented at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference linked air pollution, particularly from wildfire smoke, to an elevated risk of dementia. The research, focusing on Southern California, suggested that the unique composition of wildfire smoke, with its higher concentration of toxic chemicals, poses a significant threat to brain health.

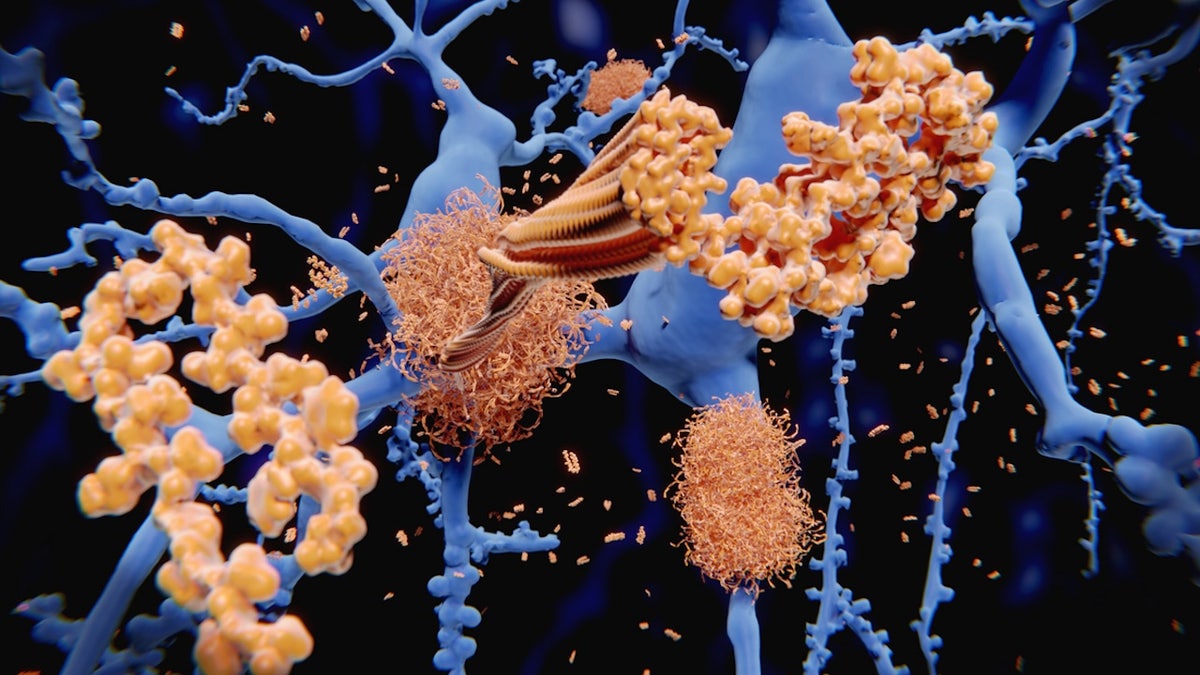
5. Defining Alzheimer's Through Biological Changes in the Brain
Groundbreaking research published in June 2024 revealed physical changes in the brain caused by Alzheimer's disease. This research signifies a shift towards defining the disease based on biological processes, much like cancer or heart disease. These physical alterations precede the typical outward symptoms of memory loss and cognitive decline, offering potential avenues for earlier diagnosis and intervention.
For more information and resources, visit the Alzheimer's Association website at www.alz.org.








